David Nam, Judith Mantell, David Bull, Paul Verkade, Alin Achim
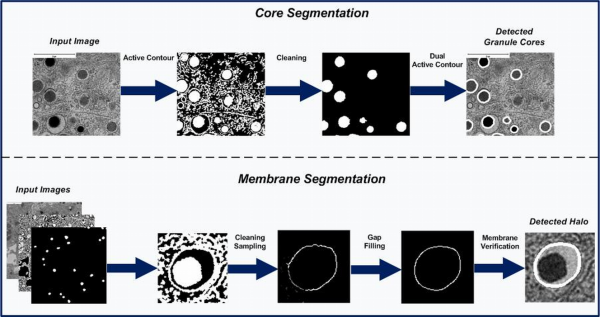
The following work presents a graphical user interface (GUI), for automatic segmentation of granule cores and membranes, in transmission electron microscopy images of beta cells. The system is freely available for academic research. Two test images are also included. The highlights of our approach are:
- A fully automated algorithm for granule segmentation.
- A novel shape regularizer to promote granule segmentation.
- A dual region-based active contour for accurate core segmentation.
- A novel convergence filter for granule membrane verification.
- A precision of 91% and recall of 87% is observed against manual segmentations.
Further details can be found in–
D. Nam, J. Mantell, D. Bull, P. Verkade, and A. Achim, “A novel framework for segmentation of secretory granules in electron micrographs,” Med. Image Anal., vol.18, no. 2, pp. 411–424, 2014.