Fan Zhang, Mariana Afonso and David Bull
ABSTRACT
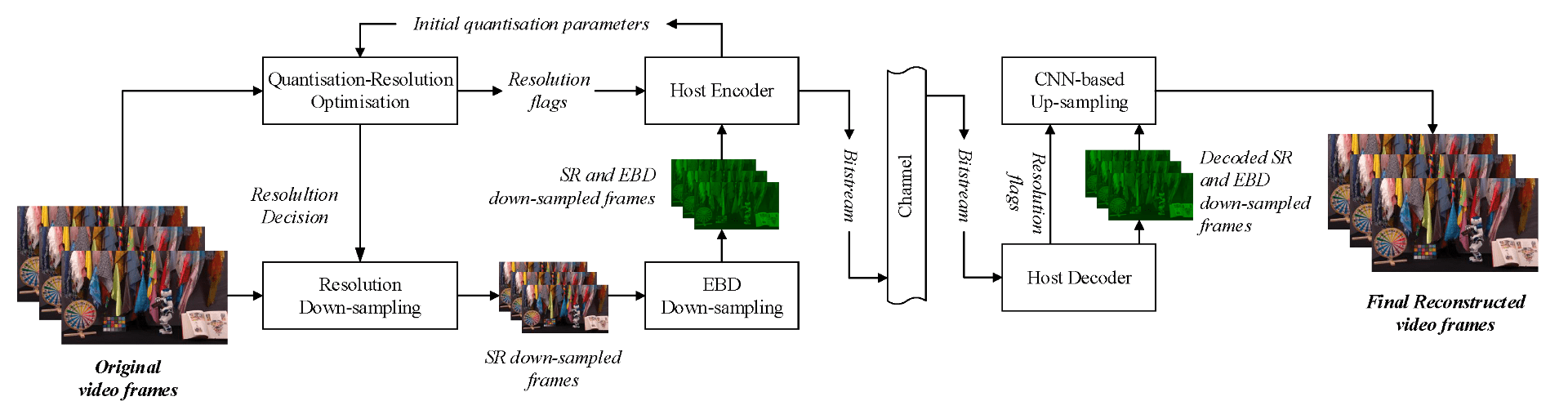
We present a new video compression framework (ViSTRA2) which exploits adaptation of spatial resolution and effective bit depth, down-sampling these parameters at the encoder based on perceptual criteria, and up-sampling at the decoder using a deep convolution neural network. ViSTRA2 has been integrated with the reference software of both the HEVC (HM 16.20) and VVC (VTM 4.01), and evaluated under the Joint Video Exploration Team Common Test Conditions using the Random Access configuration. Our results show consistent and significant compression gains against HM and VVC based on Bjonegaard Delta measurements, with average BD-rate savings of 12.6% (PSNR) and 19.5% (VMAF) over HM and 5.5% (PSNR) and 8.6% (VMAF) over VTM.
PROPOSED ALGORITHM
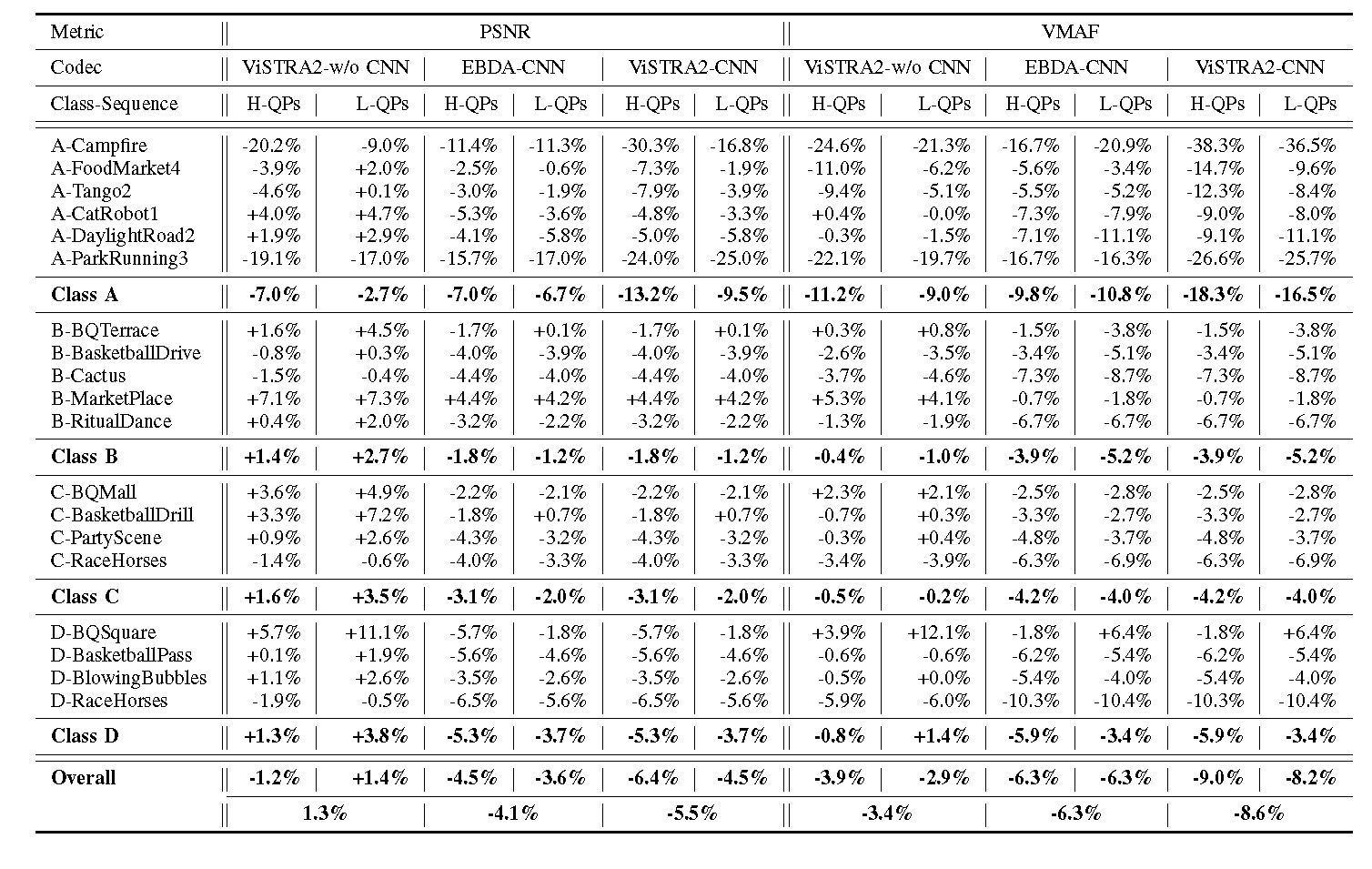
RESULTS
BD-rate results of ViSTRA2 when HM 16.20 was employed as host codec.

BD-rate results of ViSTRA2 when VTM 4.01 was employed as host codec.
REFERENCE
[1] F. Zhang, M. Afonso and D. R. Bull, ViSTRA2: Video Coding using Spatial Resolution and Effective Bit Depth Adaptation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.02833.
[2] M. Afonso, F. Zhang and D. R. Bull, Video Compression based on Spatio-Temporal Resolution Adaptation. IEEE T-CSVT (Letter), 2019.
[3] M. Afonso, F. Zhang, A. Katsenou, D. Agrafiotis, D. Bull, Low Complexity Video Coding Based on Spatial Resolution Adaptation, ICIP, 2017.