We work on novel algorithms and systems for 3-D tracking and mapping the environment using visual information. This includes fundamental research into new techniques and working with industry to develop state of the art solutions in applications such as augmented reality and infrastructure inspection.
Current work focuses on vision-based simultaneous localisation and mapping (SLAM) systems, especially relocalisation techniques and semantic modelling, and large scale GPS-free geolocation using ground level panoramic and aerial images, based on novel techniques linking semantic information in cartesian maps to image content.
Recent industry collaborations include Innovate UK funded projects with Perceptual Robotics to develop techniques for localising and tracking drones with respect to wind turbines for surface inspection and work with Condense Reality on volumetric capture as part of the BT led 5G Create project Edge-XR.
Contact: Professor Andrew Calway
Recent Projects
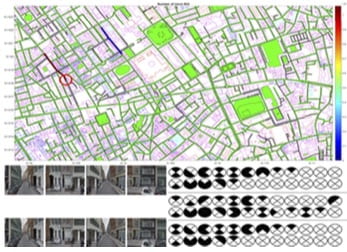
AUTOMATED MAP READING USING SEMANTIC FEATURES New research on localising images in 2-D cartographic maps by linking semantic information, akin to human map reading. Based on minimal binary route patterns indicating presence or absence of semantic features and trained networks to detect such features in images. Leads to highly scalable map representations. [IROS 2018 paper][Project page] |
OUT-OF-VIEW MODEL-BASED TRACKING
3-D model-based tracking which uses a trained network to predict out-of-view feature points, allowing tracking when only partial views of an object are available. Designed to deal with tracking scenarios involving large objects and close view camera motion.
[IROS 2018 paper]
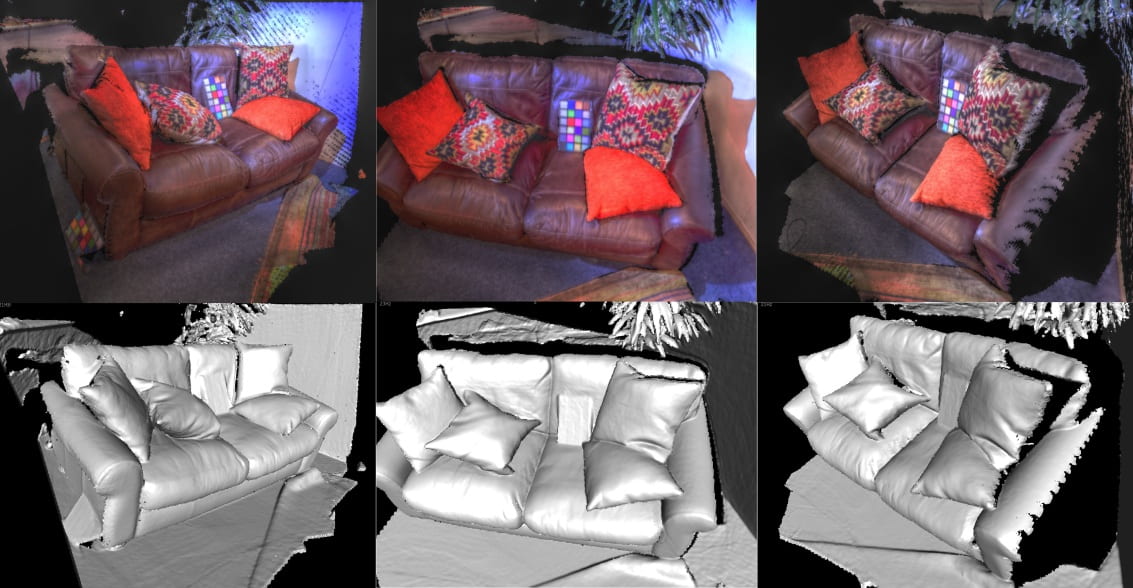
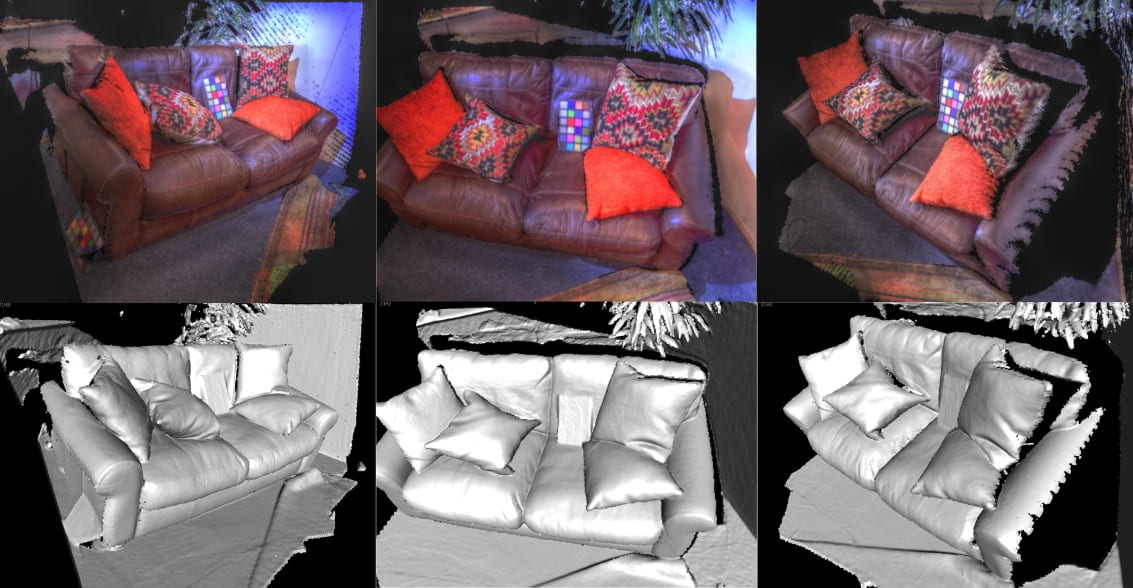
HDRFUSION: RGB-D SLAM WITH AUTO EXPOSURE
RGB-D SLAM system which is robust to appearance changes caused by RGB auto exposure and is able to fuse multiple exposure frames to build HDR scene reconstructions. Results demonstrate high tracking reliability and reconstructions with far greater dynamic range of luminosity.
[3DV 2016 paper][Project page]
LDD PLACE RECOGNITION
Place recognition using landmark distribution descriptors (LDD) which encode the spatial organisation of salient landmarks detected using edge boxes and represented using CNN features. Results demonstrate high accuracy for highly disparate views in urban environments.
[ACCV 2016 paper][Project page]
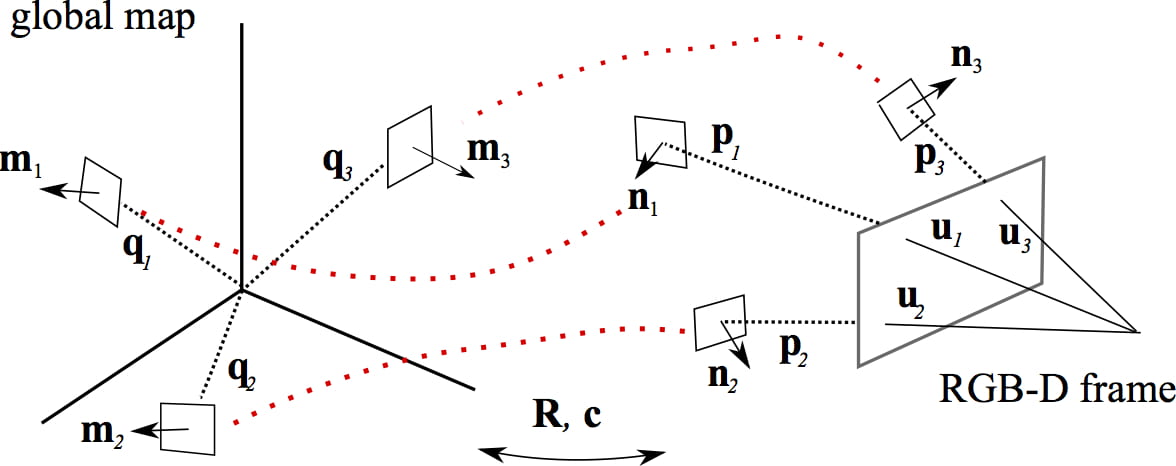
MULTI-CORRESPONDENCE 3-D POSE ESTIMATION
Novel algorithm for estimating the 3-D pose of an RGB-D sensor which uses multiple forms of correspondence – 2-D, 3-D and surface normals – to gain improved performance in terms of accuracy and robustness. Results demonstrate significant improvement over existing algorithms.
[ICRA 2016 paper][Project page]
RGB-D RELOCALISATION USING PAIRWISE GEOMETRY
Fast and robust relocalisation in an RGB-D SLAM system based on pairwise 3-D geometry of key points encoded within a graph type structure combined with efficient key point representation based on octree representation. Results demonstrate that the relocalisation out performs that of other approaches.
[ICRA 2015 paper][Project page]